Ongrid/Offgrid/Hybrid
Types of solar systems (On-grid, Off-grid and Hybrid) and their use cases
In the feat to achieve grid parity – homeowners, decision-makers, architects, industrialists and businesses are making a foray into the world of sustainable energy. Grid parity is a stage where alternative energy can generate electricity at a Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). It means the point when electricity from solar cost can break even or cost you less than electricity from the local grid.
A solar system is made of the following components;
Solar panels
Inverter
DC protection system
AC protection panel
Batteries
Factors that determine the selection of solar systems are;
The accessibility to electricity
Frequency in power outages
Number of equipment required for energy production
The cost of residential/commercial electricity
Following are three types of solar systems available in the market for investors to opt for;
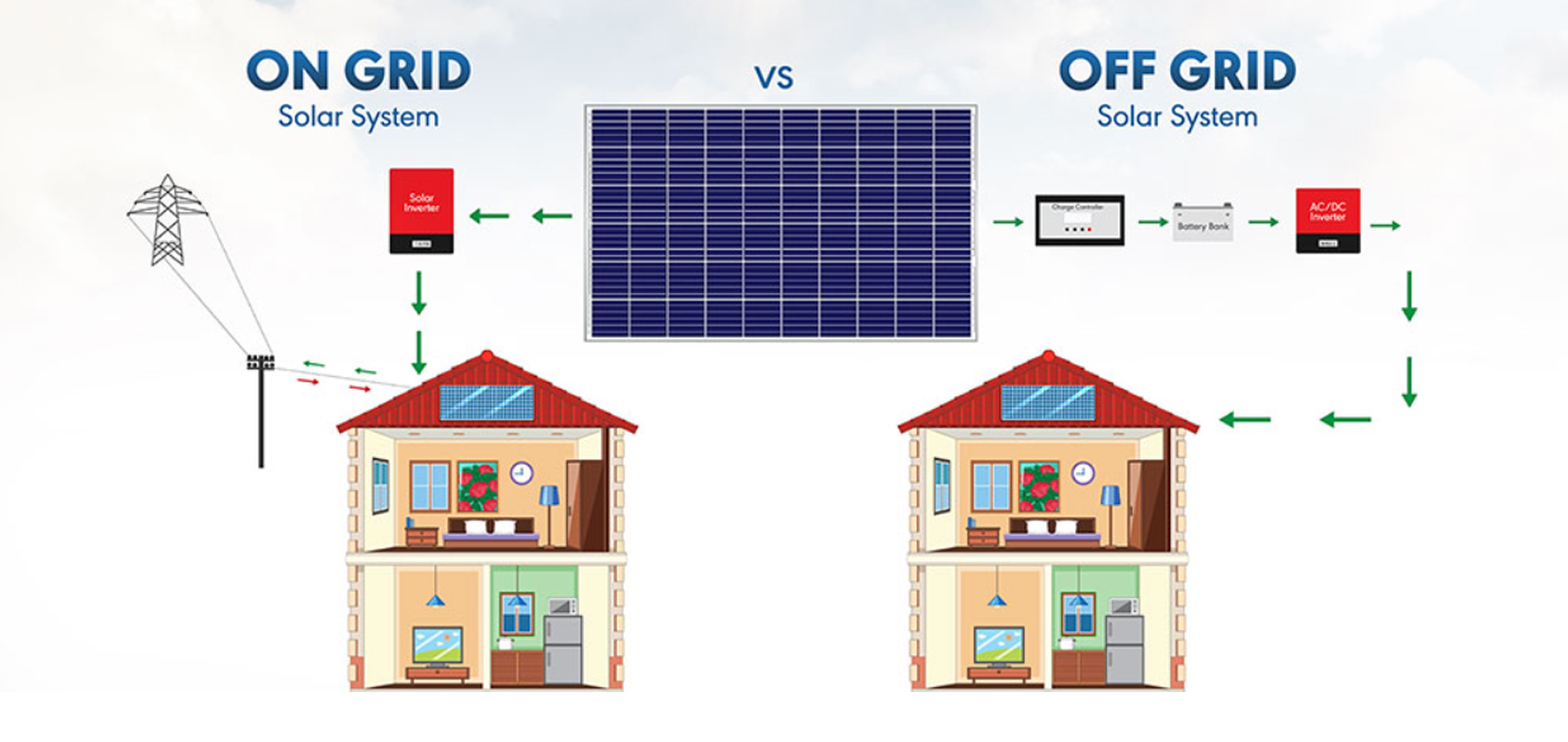
ON-GRID SOLAR SYSTEMS
Here, the systems are tied to the local utility grids and they act as a complementary source of electricity. Further, Investors can supplement the low energy yield with the grid or transfer the surplus energy produced by the solar system to the grid via net metering to get compensated for the same.
However, in case of a power shutdown, your electricity supply will be affected if it is not tied to a battery backup system. Even if your solar system can accommodate your monthly electricity usage, you will be charged the basic service fee and demand charges for grid connection. When you have a commercial connection, you are often levied to pay an enhanced rate of electricity during a peak period.
It assists you in earning a faster return on investment (ROI), lower electricity overheads and savings through netmetering.
Components employed in on-grid systems – Panels, Meters, Grid-tied inverters and the local grid
Use Cases – Suitable for residential, commercial, industrial properties with robust grid availability
OFF-GRID SOLAR SYSTEMS
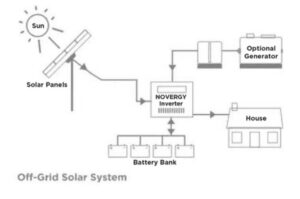
Widely known as standalone systems, they are systems that help you in building a self-reliant powerhouse on your premises. Here, the MPPT(Maximum Power Point Tracker) helps the PV array to charge the battery bank, then transfer it to the inverter. Hereafter, the inverter sends the current to the AC load to support the energy demands at night and during the outcast as well.
The system needs to be engineered and designed seamlessly to uphold the energy demands in peak times. The batteries and inverters play a very crucial role in the successful installation of these systems. However, if everything is assembled well, the system will remain unaffected by the changing weather patterns and acute power outages. The upfront cost is generally higher than the grid-tied systems as it needs complementary elements like batteries for energy storage.

These systems are independent of the local grid and offer higher ROI while ensuring complete peace of mind.
Components employed in off-grid systems – Solar Panel array, batteries and inverters
Use Cases – They are viable for agricultural lands, industrial properties, rural and remote areas and construction sites.
Hybrid solar systems
Hybrid systems are solar systems that are dependent on the grid and can also accumulate extra electricity in a storage unit. Here, the extra energy produced by the solar system after the energy consumption by appliances is transferred to the battery bank. Once they are completely charged, they can export the extra energy to the grid.
These systems deliver the functionality of both off-grid and grid-tied systems, at once. They are a more steady, secure and cost-effective way for power generation as compared to the other systems we mentioned earlier. Because it does not necessitate you to invest in large storage systems. This is the reason why they are more popular among solar investors, they remain unharmed because blackouts don’t hamper their yield or supply.
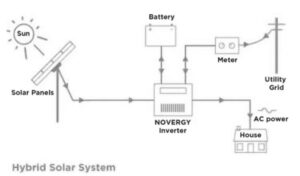
Components employed in hybrid systems – Solar Panel array, batteries and inverters, meter and grid
Use Cases – They are best suited for the agricultural sector, residential applications, micro-grids, rural areas and offices.
